- Definition of the functor
RSTR -
The functor
RSTRis a functor for a free modification further specifying the governing noun. TheRSTRfunctor is assigned to such adnominal modifications that neither meet the conditions for being considered adverbal modifications nor do they belong among other (more clearly defined) adnominal modifications.
The functor RSTR is the least specific adnominal functor. We assign this functor to such adnominal modifications to which it would not be natural to assign a verbal functor and which do not fulfil the semantic requirements of other adnominal functors.
!!! The original plan to distinguish restrictive and descriptive adnominal modifications has been abandoned. Both types of modification are assigned the functor RSTR.
Valency. The RSTR modification is always a non-valency modification.
Forms. The basic forms of modifications with the functor RSTR are:
-
agreeing form of an adjective.
Example:
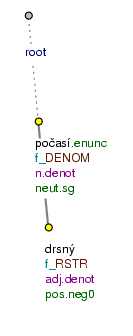
drsné.
RSTRpočasí (=rough weather) Fig. 7.59po mozkové.
RSTRmrtvici (=after a cerebral apoplexy)proti destruktivnímu.
RSTRzpůsobu hry (=against the destructive way of playing)sedící.
RSTRžena (=a sitting woman)NB! Also numeral expressions with the function of an attribute belong here as well (for details see Section 10.1.1, "Numerals with the role of an attribute (
RSTR)"). E.g.:několik.
RSTRměsíců (=a few months)pět.
RSTRdětí (=five children)dvojí.
RSTRstátní občanství (=double nationality)více.
RSTRpeněz (=more money) -
possessive adjective.
Example:
Karlova.
RSTRuniverzita (=Charles University)papinův.
RSTRhrnec (=Papin's pot) -
agreeing form of a noun.
Example:
Karel.
RSTRNovák (=Karel Novák)rozhodčí.
RSTRSeverýn (=the referee Severyn)Prostřelil libereckého brankáře.
RSTRMaiera (=he shot through the Liberec goalman Maier)v Praze - Dejvicích.
RSTR(=in Prague - Dejvice)do města Prahy.
RSTR(=to the city of Prague) -
noun in a non-prepositional case form.
The most common forms:
genitive kapacita 200 míst (=the capacity of 200 places); ve výši asi 30 miliard korun (=in the amount of 30 billions of Crowns); míra nezaměstnanosti 2,8 procenta (=the rate of unemployment of 2,8 percent) -
prepositional phrase.
The most common forms:
k+3 doklady k favoritu (=the documents for Skoda Favorit) na+4 konve na mléko (=milk cans); jízdenku na vlak (=train ticket) na+6 výrobní linka na bázi nové technologie (=an assembly line based on the new technology) o+6 loď o výtlaku 9700 tun (=a ship with shipload 9700 tons) po+6 propast po berlínské zdi (=a gap after the Berlin wall); stopy po chybných rozhodnutích (=the traces after the wrong decisions) pod+7 zóny pod kontrolou UNPROFOR (=zones under the control of UNPROFOR) s+7 zájezd se sportovním programem (=a trip with a sports programme) ve formě+2 výhra ve formě zájezdu (=a prize in the form of a trip) v+6 civilizace ve dnešní podobě (=civilization in today's form); plavkyně v počtu osmi (=lit. swimmers in number (of) eight) v podobě+2 bariéry v podobě státní správy (=the barriers in the form of state administration) z+2 daně z přidané hodnoty (=value added tax) za+4 škoda za 171 000 korun (=the loss of 171 000 Crowns) -
relative clause.
For more on dependent relative clauses see Section 5, "Dependent verbal clauses".
Example:
Udeřil i toho, kdo si to nezasloužil.
RSTR(=He hit also the one who did not deserve it.)The RSTR functor is also assigned to some dependent clauses introduced by the subordinating conjunction že. Example:
Důsledkem neuspokojivě řešené dnešní situace ve vztahu k minulosti je také fakt, že se vytvořily.
RSTRdvě výrazně oddělené názorové skupiny. (=The result of the unsatisfactorily resolved present situation in relation to the past is also the fact, that two groups were formed with dramatically different opinions.)
NB! The RSTR functor is also assigned to modifications dependent on certain proper nouns and names (for more see Section 8.2.1, "Specific rules for certain types of proper nouns"). Example:
Jablonec nad Nisou.RSTR (=Jablonec nad Nisou)
náměstí Míru.RSTR (=the Peace square)
Karlův.RSTR most (=Charles Bridge)
NB! The RSTR functor is also used when representing certain specific structures like addresses, laws and public notices; see Section 12.1, "Identification of statutes and regulations" and Section 12.2, "Addresses").
The functor RSTR is the least specific functor. We assign it in those cases when the semantics of the modification is not very specific, therefore, there are a number of borderline cases.
Border with the functor ID. The RSTR modification can get very close to the ID modification. In such cases it is important whether the given modification has regular inflected forms and also what is the nature of the given entity (person vs. thing). For more precise rules see Section 11.4, "Dependency relations in noun phrases (two nouns in the same form)". Compare:
-
město Bratislava.
ID(=the city of Bratislava.NOM)Jedeme do města Bratislavy.
RSTR(=We drive to the city of Bratislava.GEN) -
město Groznyj.
ID(=the city of Groznyj)Jedeme do města Groznyj.
ID(=We drive to the city of Groznyj.) -
kamarád.
RSTRJan (=(my) friend Jan)kamarád.
RSTRJohn (=(my) friend John)
Border with the functor INTF. The functor RSTR can get close to the functor INTF, especially in those cases, where the modification is expressed by the pronoun ten (=the_one) (or on (=he)). For more on this see Section 7.2.1, "Borderline cases with the INTF functor".
Borders with the functors AUTH and APP. The functor RSTR borders on the adnominal functors AUTH and APP (in cases like: Karlova.RSTR knížka (=Charles' book) vs. Nezvalovy.AUTH básně (=Nezval's poems)). For more on this see Section 10.2.1, "Borderline cases with the functor AUTH".
Borders with adverbal functors. The functor RSTR borders on a number of other functors, mainly those of adverbal modifications - especially in those cases in which the modification is expressed by a prepositional phrase. No clear rules for determining the functor has been established so far. Generally, it can be said that the RSTR functor is assigned if it is not possible to assign a more specific functor.