The following constructions are defined as forms:
-
heading - colon - entered data.
Example:
Atény : jasno 32 / 22 (=Athens: fine 32 / 22)
Berlín: přeháňky 27 / 14 (=Berlin: showers 27 / 14)
Bratislava: jasno 24 / 12 (=Bratislava: fine 24 / 12)
Budapešť: jasno 28 / 18 (=Budapest: fine 28 / 18)
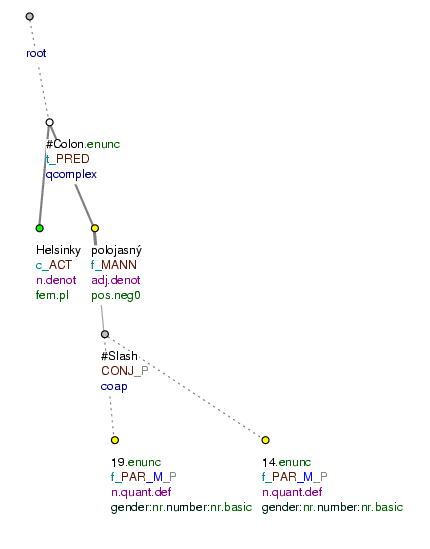
Helsinky: polojasno 19 / 14 (=Helsinki: clear spells 19 / 14)
Example:
Figure : 3
Kancelář: Rekrea (=Office: Rekrea)
Oblast: ČR - Jeseníky (=Region: Czech Republic - Jeseníky)
Ubytovací zařízení: Penzion Brněnka (=Accommodation facilities: Brněnka Guest House)
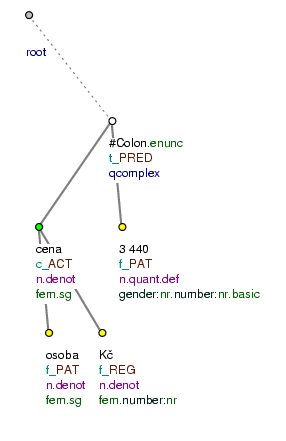
Cena za osobu Kč: 1 890 (=Price per person Kč: 1 890)
Dítě: Do 7 let zdarma pobyt i strava (=Child: Under 7 years accommodation and meals free)
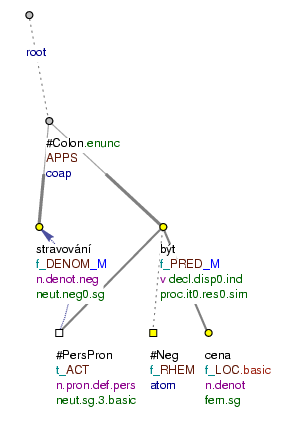
Stravování: V ceně pobytu je záloha 60 Kč na den (=Meals: The price of the accommodation includes a deposit of 60 Kč per day)
Doprava: Vlastní , autobus Branná , vlak Ostružné . (=Transport: Own transport or bus to Branná, train to Ostružné.)
Popis: Penzion leží asi 2,5 km od Branné v okrese Šumperk v klidné krajině. (=Description: The guest house is situated approximately 2.5 km from Branná in Šumperk district, in peaceful countryside.)
Forms are represented as simple verbal clauses in which the effective root is represented by a node standing for a colon between the heading and the data entered (t_lemma=#Colon; functor=PRED). The effective root of the heading is assigned the functor ACT and the effective root of the data entered is usually a Patient.
Cf.:
-
Figure: 1
The construction is represented as a verbal clause. The effective root is represented by a node standing for a colon (
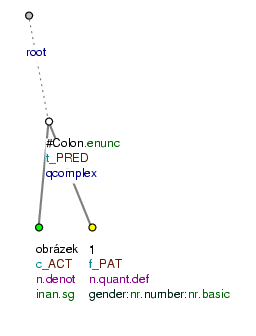
t_lemma=#Colon;functor=PRED). The effective root of the heading (the node representing the noun obrázek) is assigned the functorACT, and the effective root of the data entered (the node representing the number 1) is assigned the functorPAT. Cf. Fig. 8.235. -
Figure 1
The construction is not represented as a verbal clause. The node representing the number 1 is assigned the functor
RSTRand is dependent on the node for the noun obrázek, which is assigned the functorDENOM.
If one part of the form (usually the data entered) consists of a clause with a finite verb form, then the relationship between the two parts (head and data entered) is represented as an appositional relationship (cf. for example: Fig. 8.237). More complex constructions are treated in such a way as to ensure that they correspond as closely as possible to the basic rules of annotation on the tectogrammatical level. If appropriate, an empty verb is inserted both in the left-hand part of the form and in the right-hand part (cf. for example: Fig. 8.238, Fig. 8.239 and Fig. 8.240).
Examples and model trees:
Helsinky polojasno 19 / 14. (=Helsinki: clear spells 19 / 14.) Fig. 8.236
Stravování: Není v ceně. (=Meals: Not included in the price.) Fig. 8.237
Cena za osobu Kč: 3 440. (=Price per person Kč: 3 440.)
(=the price per person in Crowns is 3,440) Fig. 8.238
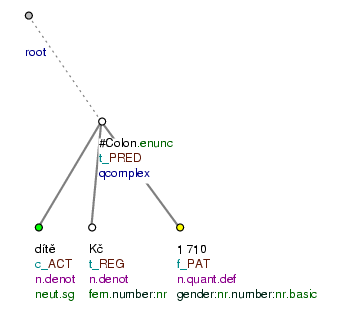
Dítě Kč: 1 710. (=Child Kč: 1 710.) Fig. 8.239
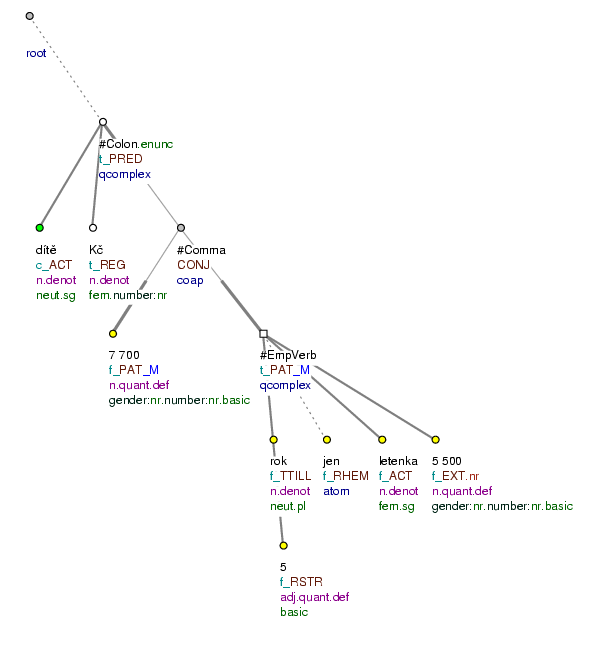
Dítě Kč: 7 700, do 5 let jen letenka za 5 500. (=Child Kč: 7,700, under 5 years flight only 5,500.) Fig. 8.240