The guidelines for the annotation of questions are almost the same as for the annotation of declarative clauses, nevertheless the surface word order of questions is often different.
In subsequent sections we describe separately guidelines for yes-no questions (see Section 4.4.1, "Topic-focus articulation of yes-no questions"), wh-questions (see Section 4.4.2, "Topic-focus articulation of wh-questions") and for indirect questions (see Section 4.4.3, "Topic-focus articulation of indirect questions").
In Czech, there are two ways to form yes-no questions: using intonation or inverse word order.
Questions formed using intonation. If a question is formed using intonation, the word order of the corresponding declarative clause is preserved and so is its topic-focus articulation. Contextually bound expressions are usually placed before the governing node of the question, contextually non-bound expressions to the right from it, with the focus proper placed rightmost.
Examples:
Letos [tfa=t] v létě [tfa=t] pojedeš [tfa=f/t] NA HORY [tfa=f] ? (=lit. This_year in summer (you) will_go to mountains?) Fig. 10.26
Na hory [tfa=c] pojedeš [tfa=f] letos [tfa=f] V LÉTĚ [tfa=f] ? (=lit. To mountains (you) will_go this_year in summer?)
Na hory [tfa=c] letos [tfa=t] pojedeš [tfa=t] V LÉTĚ [tfa=f] ? (=lit. To mountains this_year (you) will_go in summer?)
Na hory [tfa=c] letos [tfa=t] v létě [tfa=t] POJEDEŠ [tfa=f] ? (=lit. To mountains this_year in summer (you) will_go?)
Even in the case of yes-no questions formed using intonation, the verb can apper on the second position in the sentence (for that see Section 1.1, "Surface word order").
Example:
Letos [tfa=c] pojedeš [tfa=t] v létě [tfa=t] NA HORY [tfa=f] ? (=lit. This_year (you) will_go in summer to mountains?)
Questions formed using inverse word order. If a question is formed using inverse word order, the situation is more complex:
-
the node representing the expression carrying the intonation centre of the question is assigned the
tfavaluefand moved (with respect to the surface word order) to the rightmost position (on the rightmost path) as the focus proper of the question. -
the governing verb (even though it is in the initial position in the question) is considered (if not repeated from the preceding context) to be the least communicatively dynamic contextually non-bound expression. The node representing the governing verb is therefore assigned the
tfavaluef, and if it does not constitute the focus proper, all its contextually bound dependent nodes are placed to the left from it and all its contextually non-bound dependent nodes to the right from it.As the verb occupies the initial position, it cannot signal the division between contextually bound and non-bound expressions as usual. The only clue apart from the semantics is a violation of the systemic ordering.
Example:
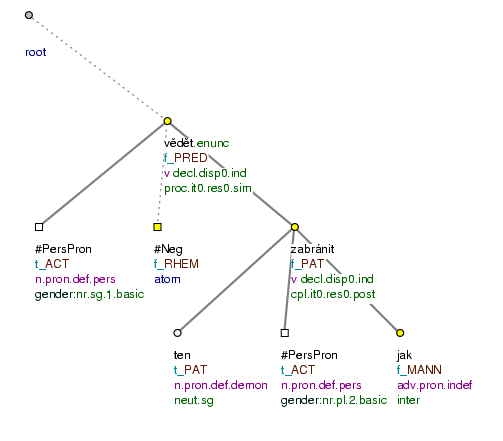
Pojede [
tfa=f] Jirka [tfa=c] letos [tfa=t] v létě [tfa=t] NA HORY [tfa=f] ? (=lit. Will_go George this_year in summer to mountains?) Fig. 10.27 -
nodes representing contextually non-bound expressions have the same order as in the surface word order if they are between the node for the verb and the focus proper.
-
nodes representing (contrastive or non-contrastive) contextually bound direct modifications of the verb have the values
torcand are ordered according to the guidelines for the ordering of nodes in verbal groups, which are described in Section 3.2.2, "Ordering of contextually bound nodes in verbal groups".
Examples:
(Postmodernismus.) Nastane [tfa=f] nyní [tfa=t] na Zábradlí [tfa=t] postmodernistická [tfa=t] éra [tfa=f] ? (=lit. (Postmodernism.) Will_there_be now at Zábradlí (a) postmodern era?) Fig. 10.28
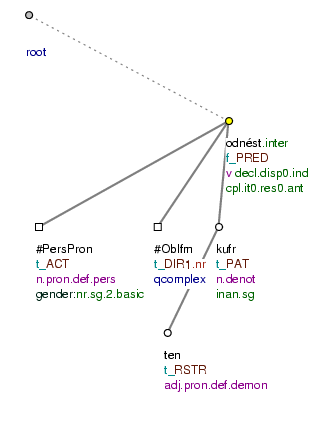
Odnesl jsi [tfa=f] ten [tfa=t] kufr [tfa=t] ? (=lit. Did_you_carry_away _ the suitcase?) Fig. 10.29
A yes-no question can also exhibit the subjective order (see Section 1.1, "Surface word order"). In such cases nodes are reordered according to the same guidelines as in unmarked cases.
Example:
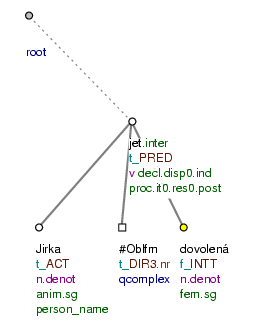
NA DOVOLENOU [tfa=f] Jirka [tfa=t] pojede [tfa=t] ? (=lit. On holiday George will_go?) Fig. 10.30
Figure 10.26. Topic-focus articulation of yes-no questions
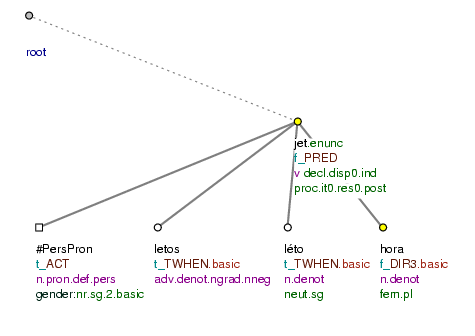
Letos v létě pojedeš na hory? (=lit. This_year in summer (you) will_go to mountains?)
Figure 10.27. Topic-focus articulation of yes-no questions
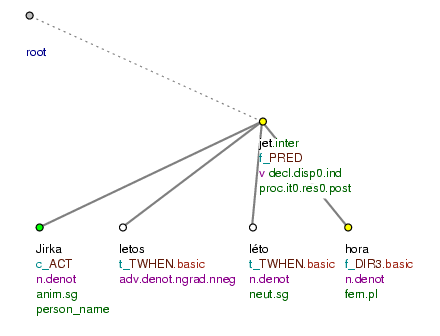
Pojede Jirka letos v létě na hory? (=lit. Will_go George this_year in summer to mountains?)
Figure 10.28. Topic-focus articulation of yes-no questions
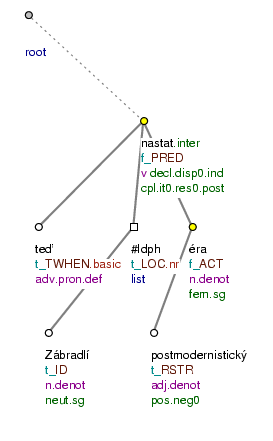
(Postmodernismus.) Nastane nyní na Zábradlí postmodernistická éra? (=lit. (Postmodernism.) Will_there_be now at Zábradlí (a) postmodern era?)
Wh-questions are formed using interrogative words. Since the interrogative expression represents what the speaker is asking, it usually constitutes the focus proper (see Section 3.1.1, "Focus proper"), but it need not be so. In examples such as Kam pojedeš NA DOVOLENOU ? (=lit. Where (you) will_go on holiday?), the focus proper is constituted by the last expression in the sentence, which at the same time carries the intonation centre (see Section 1.2.1, "Intonation centre").
Here are the guidelines for the annotation of wh-questions:
-
the node representing the interrogative expression is assigned the
tfavaluef, and provided it does not constitute the focus proper, it is placed right after the governing verb. -
the node representing the expression carrying the intonation centre in the spoken form of the sentence is assigned the
tfavaluefand is moved to the rightmost position (on the rightmost path) as the focus proper of the question.If the intonation cannot be determined unambiguously, we consider the interrogative expression to constitute the focus proper.
-
the node representing the governing verb is usually assigned the
tfavaluefand signals as usual the division between contextually bound and non-bound nodes: all its contextually bound dependent nodes are placed to the left from it and all its contextually non-bound dependent nodes to the right from it. In wh-questions, the verb quite often stands in the second position in the sentence (see Section 1.1, "Surface word order"). -
a node representing an expression standing between the interrogative expression and the verb which can be pronounced with a contrastive stress and which is not directly deducible from the preceding context is assigned the
tfavaluecand moved to the left. This applies also to expressions standing to the right from the verb.Example:
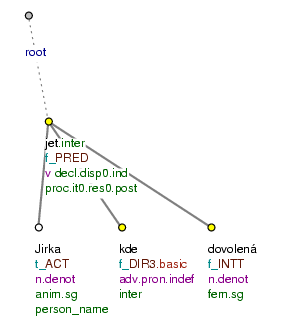
Kam [
tfa=f] Jirka [tfa=t] pojede [tfa=f] NA DOVOLENOU [tfa=f] ? (=lit. Where George will_go on holiday?) Fig. 10.31 -
nodes representing contextually bound direct modifications of the verb are assigned the
tfavaluetand are placed to the left from the node for the governing verb according to the guidelines for the ordering of nodes in verbal groups, described in Section 3.2.2, "Ordering of contextually bound nodes in verbal groups".
Examples:
Jakým [tfa=f] způsobem [tfa=t] peněžní [tfa=t] ústavy [tfa=t] , které [tfa=t] chcete na ocenění [tfa=t] nominovat [tfa=t] , vybíráte [tfa=f] ? (=lit. In_what way bank houses.ACC that (you) want to_nominate for (the) prize (you) select?) Fig. 10.32
Na dovolenou [tfa=c] pojedeš [tfa=t] KAM [tfa=f] ? (=lit. On holiday (you) will_go where?) Fig. 10.33
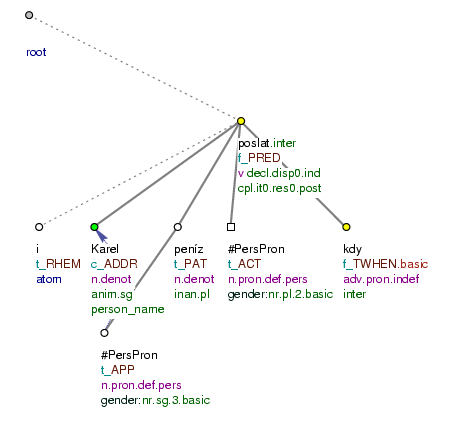
Kdy [tfa=f] pošlete [tfa=f] i [tfa=t] Karlovi [tfa=c] jeho [tfa=t] peníze [tfa=t] ? (=lit. When (you) will_send also to_Charles his money?) Fig. 10.34
Also wh-questions can exhibit the subjective order (see Section 1.1, "Surface word order"). In such cases nodes are reordered according to the same guidelines as in unmarked cases.
Example:
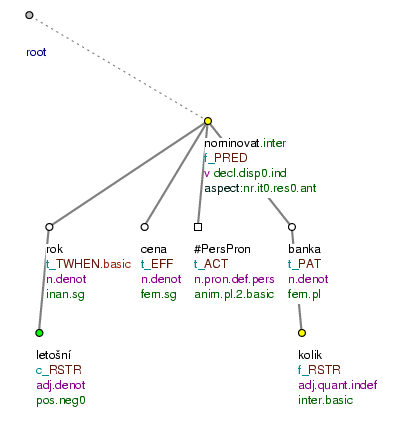
KOLIK [tfa=f] bank [tfa=t] jste v letošním [tfa=c] roce [tfa=t] na cenu [tfa=t] nominovali [tfa=f] ? (=lit. How_many banks (you) did in this year for (the) prize nominate?) Fig. 10.35
Figure 10.31. Topic-focus annotation of wh-questions
Kam Jirka pojede na dovolenou? (=lit. Where George will_go on holiday?)
Figure 10.32. Topic-focus annotation of wh-questions
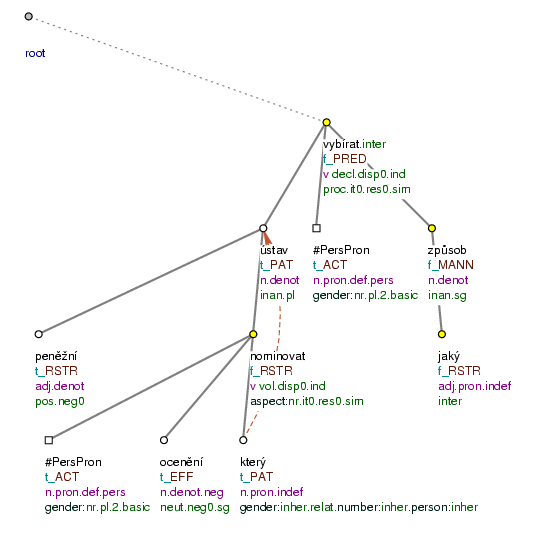
Jakým způsobem peněžní ústavy, které chcete na ocenění nominovat, vybíráte? (=lit. In_what way bank houses.ACC that (you) want for (the) prize to_nominate (you) select?)
Figure 10.33. Topic-focus annotation of wh-questions
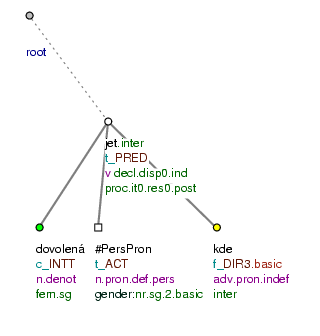
Na dovolenou pojedeš kam? (=lit. On holiday (you) will_go where?)
From the point of view of the topic-focus articulation, indirect questions behave similarly to direct questions.
The annotation of the topic-focus articulation of most indirect questions follows the guidelines for the annotation of wh-questions (see Section 4.4.2, "Topic-focus articulation of wh-questions").
Example:
Nevím [tfa=f] , jak [tfa=f] tomu [tfa=t] zabráníte [tfa=f] (=lit. (I) do_not_know how it.ACC (you) will_prevent.) Fig. 10.36
Indirect questions introduced by the expressions zda (=whether), jestli (=if) are annotated according to the guidelines for wh-queations (see Section 4.4.1, "Topic-focus articulation of yes-no questions").